
Simply select starting at LOCUS, hold down the key and scroll down the document until you see the // at the end and complete the selection to that point as shown below. This format always starts with the text LOCUS and finishes with two forward slashes (//). Many sequence-oriented web sites have the option of viewing sequences in GenBank format. While MacVector does have a built-in Entrez browser (Database | Internet Entrez Search) you can easily import GenBank formatted text into MacVector via a simple copy and paste approach. You can also join fragments together on the Cloning Clipboard by simply clicking in the circles at the end of fragments, then dragging and dropping those onto a different end. Again, if the ends are not compatible, a dialog will be displayed letting you fill or cut back the ends to force a blunt ended ligation. The Ligate button is very similar to invoking Paste, except that instead of pasting the contents of the global system clipboard, it pastes the selected fragment on the Cloning Clipboard. The Cloning Clipboard keeps a history of every fragment you have Digest’ed, though it’s easy to remove individual fragments or reset the entire clipboard. The difference between Digest and Copy is that instead of copying the fragment to the global system pasteboard, Digest copies it to MacVector’s internal Cloning Clipboard. If you select a restriction fragment, Digest becomes active. These work in a very similar manner to Copy and Paste. The sequence window Map tab has two buttons called Digest and Ligate.

Here’s an alternative approach, using the Digest and Ligate buttons and the Cloning Clipboard. We’ve previously looked at using Edit | Copy and Edit | Paste to quickly and simply create new constructs using Restriction Enzyme sites. If you have already annotated (or partially annotated) your query sequence, those features will appear in the grey background “overlay” pane – that stays locked to the top of the window while the hits can be scrolled underneath it. If a sequence is highly annotated, such that not all of the features are visible, simply holding the mouse over the appropriate pane will expand the pane to display all of the features. MacVector 15.5 has a unique BLAST Map result tab that shows the actual annotations around the alignment location for each high scoring segment pair. The classic BLAST results show the sequence alignments, but give no indication of what features are present on the database sequence at the alignment location. One consequence of this is that, particularly for sequences of bacterial origin, most of the significant hits are to entire genomes. With the advent of cheap Next Generation Sequencing technologies, there has been an explosion of whole genome sequences deposited in BLAST databases. The appearance of the ORFs can be controlled using the Options | Default Symbols menu item. there is another ATG codon upstream, that ORF will be displayed. However, if a potentially longer ORF is present, e.g. Finally, the Suppress annotated CDS ORFs check box prevents the display of ORFs that are already annotated. Codons after stops are starts is useful if you just want to know the locations of the longest possible ORFs in a sequence, irrespective of the existence of a start codon. 5’ ends are starts and 3’ ends are stops are used for linear sequences and will display ORFs coming into the sequence that do not have a start codon, or ORFs that read out of the sequence without a stop codon. The Minimum Number of Codons setting is fairly obvious. The setting for this are controlled by the MacVector | Preferences | DNA Map pane, along with the automatic Show restriction sites settings.
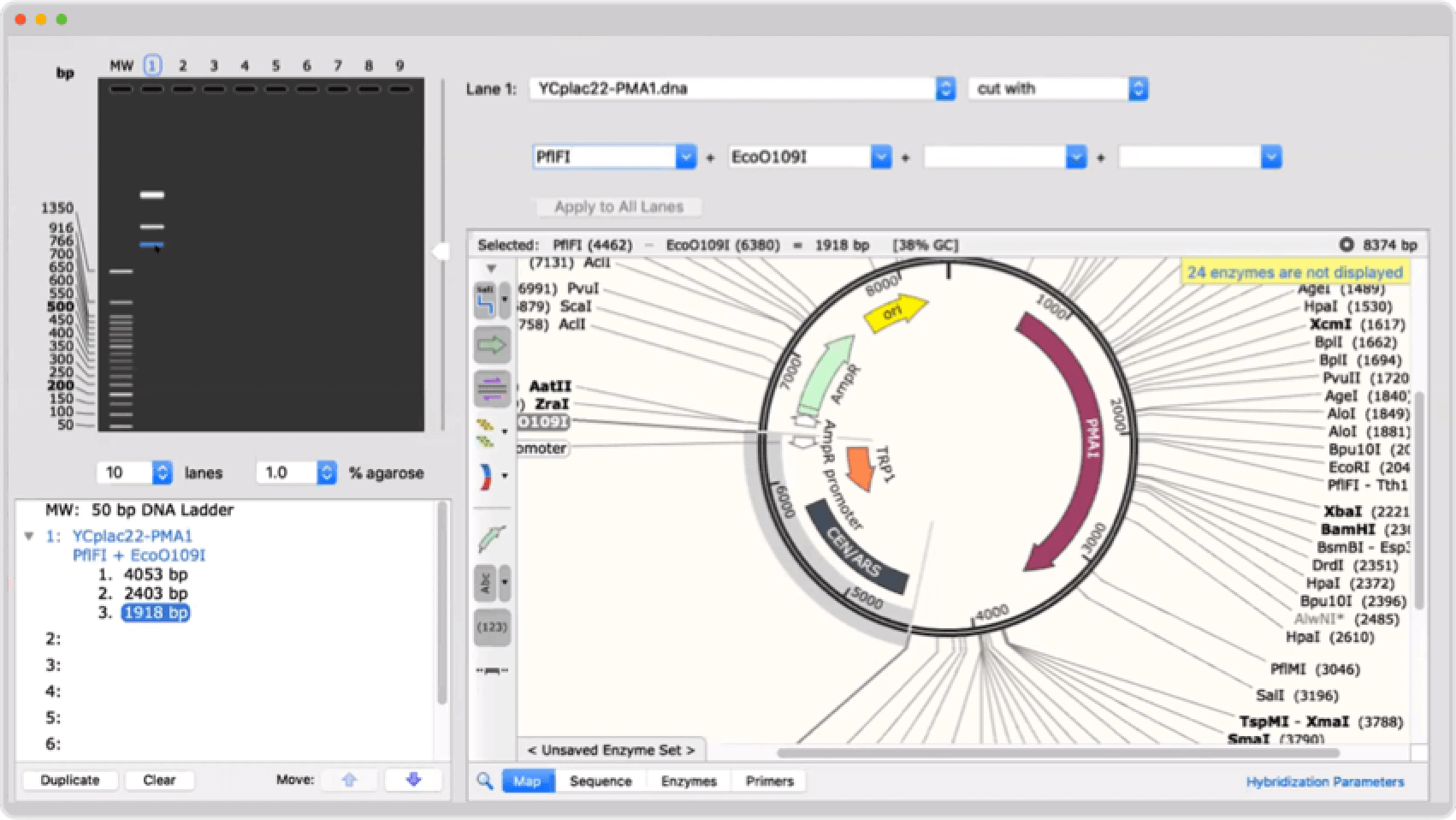
MacVector 15.5 automatically scans every DNA sequence window for open reading frames and displays the results in the Map tab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
